
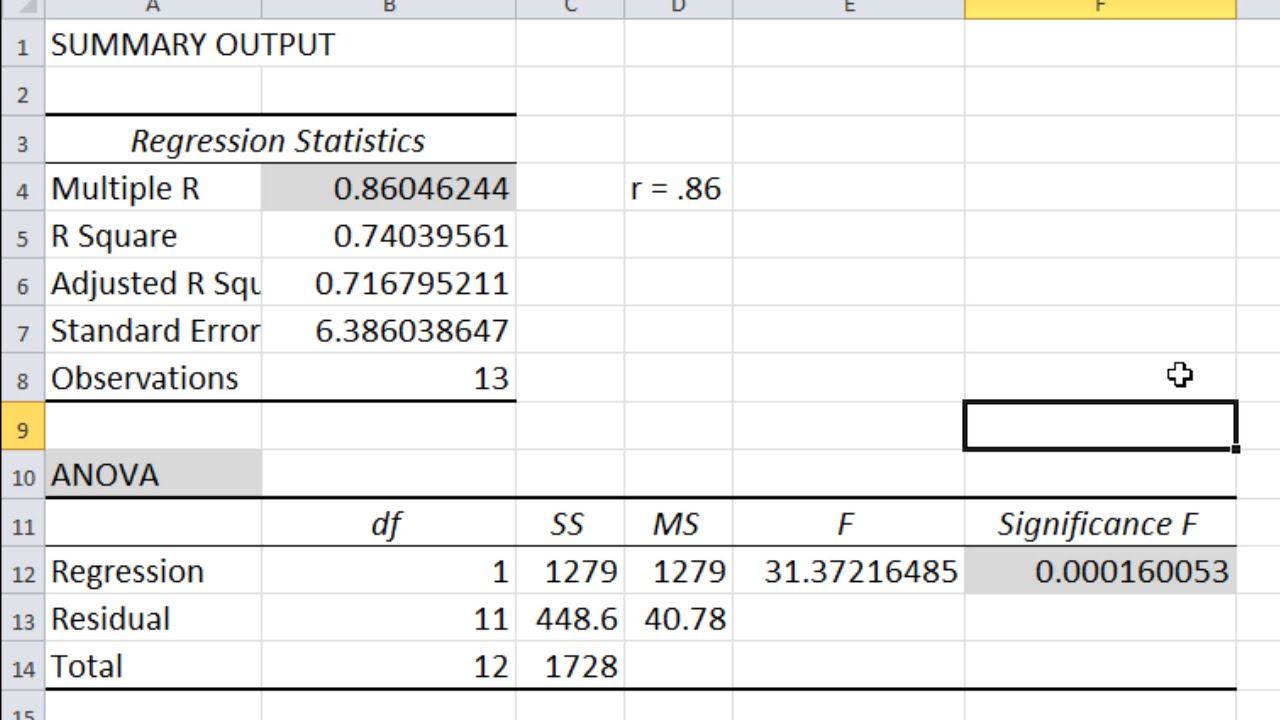
The red vertical lines represent the two-tailed critical values, and the green vertical lines the one-tailed critical values when α =. Figure 13.1 Distribution of t Scores (With 24 Degrees of Freedom) When the Null Hypothesis Is True. Thus the p value is the proportion of t scores that are +1.50 or above or that are −1.50 or below-a value that turns out to be. For now, let us define extreme as being far from zero in either direction. The probability of a t score at least this extreme is given by the proportion of t scores in the distribution that are at least this extreme. Consider, for example, a t score of +1.50 based on a sample of 25.

(There are 24 degrees of freedom for the distribution shown in Figure 13.1.) The important point is that knowing this distribution makes it possible to find the p value for any t score. Its precise shape depends on a statistical concept called the degrees of freedom, which for a one-sample t test is N − 1. As shown in Figure 13.1, this distribution is unimodal and symmetrical, and it has a mean of 0. The reason the t statistic (or any test statistic) is useful is that we know how it is distributed when the null hypothesis is true. SD is the sample standard deviation and N is the sample size. (A test statistic is a statistic that is computed only to help find the p value.) The formula for t is as follows:Īgain, M is the sample mean and µ 0 is the hypothetical population mean of interest. But finding this p value requires first computing a test statistic called t. To decide between these two hypotheses, we need to find the probability of obtaining the sample mean (or one more extreme) if the null hypothesis were true. The alternative hypothesis is that the mean for the population is different from the hypothetical population mean: μ ≠ μ0. The null hypothesis is that the mean for the population (µ) is equal to the hypothetical population mean: μ = μ0. The one-sample t test is used to compare a sample mean ( M) with a hypothetical population mean (μ0) that provides some interesting standard of comparison. In this section, we look at three types of t tests that are used for slightly different research designs: the one-sample t test, the dependent-samples t test, and the independent-samples t test.
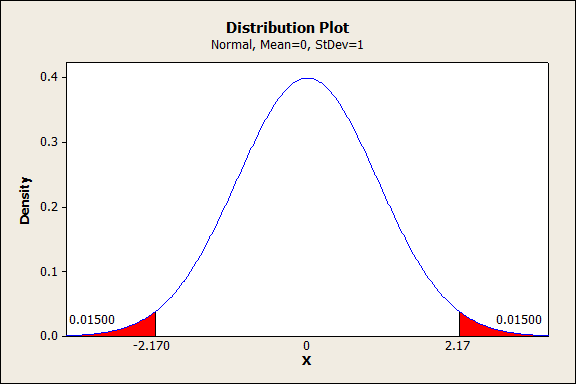
The most common null hypothesis test for this type of statistical relationship is the t test. The t TestĪs we have seen throughout this book, many studies in psychology focus on the difference between two means.
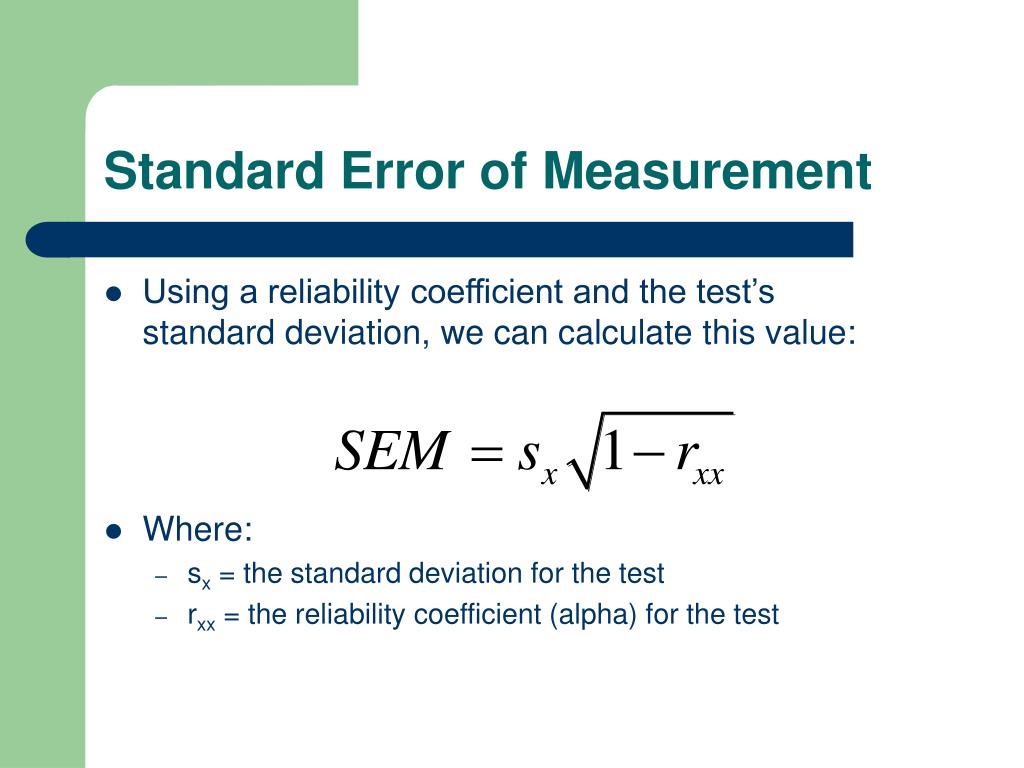
In most cases, the online statistical analysis tools mentioned in Chapter 12 will handle the computations-as will programs such as Microsoft Excel and SPSS. The emphasis here is on providing enough information to allow you to conduct and interpret the most basic versions. In this section, we look at several common null hypothesis testing procedures. Conduct and interpret null hypothesis tests of Pearson’s r.Interpret the results of one-way, repeated measures, and factorial ANOVAs.Conduct and interpret one-sample, dependent-samples, and independent-samples t tests.500, the Bonferroni-adjusted p-value reported would be 1.000 and not 1.500, which is the product of. With respect to the previous example, this means that if an LSD p-value for one of the contrasts were. The reason for this is that probabilities cannot exceed 1. In such cases, the Bonferroni-corrected p-value reported by SPSS will be 1.000. 05, we would conclude that the difference was significant.įinally, it's important to understand what happens when the product of the LSD p-value and the number of comparisons exceeds 1. To obtain the corrected p-value, we simply multiply the uncorrected p-value of. Suppose the LSD p-value for a pairwise comparison is. 05 and there were three pairwise comparisons? It's very simple. What does this mean in the context of the previous example, in which alpha was set at. Take the observed (uncorrected) p-value and multiply it by the number of comparisons made. SPSS and some other major packages employ a mathematically equivalent adjustment. 05, and three comparisons, the LSD p-value required for significance would be. Second, use the number so calculated as the p-value for determining significance. First, divide the desired alpha-level by the number of comparisons. Statistical textbooks often present Bonferroni adjustment (or correction) in the following terms. This adjustment is available as an option for post hoc tests and for the estimated marginal means feature. SPSS offers Bonferroni-adjusted significance tests for pairwise comparisons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
